Now that you understand the importance of a product prototype for your company, it is time to build one. Here we shall be addressing how to go about developing a prototype that fulfils all your needs at this stage of your start-up. Remember at this stage, it is not meant to validate your idea but to convince the external stakeholders of the feasibility and viability of your idea. Of course, the business model is as important in this respect but we shall discuss it in-depth in the next phase.
How to Develop a Perfect Prototype of Your Startup?
Since at this stage, it is the external stakeholders that you are presenting to, a bare-bones validation structure like POC will not work. You would want something more refined, more polished for it to be convincing. You would not want just a visual prototype at this stage, but a presentation prototype or proof of concept, which will not only look like the final product but also provide a demonstration of the core product functionality and design.
Know Your Software/Hardware Options
Your product might be an application or a physical object. So you would want to know which software suite you would need to rapidly develop the prototype. There is software available today that can be used to develop high-fidelity prototypes that mimic animations, touch interactions etc. For physical objects, 3D printing is widely used to quickly get working prototypes. But the first step should be to know all the options available to you before you decide to start the prototyping process.
Reverse-Engineer Competing Products
If the product that you intend to build is already in the market, it would be wise to disassemble and take the competitors’ products apart to understand how they have been built and how they work. Reverse-engineering helps you to not only understand the gaps but also come up with more efficient methods of production.
Decide on the Material/Tools
It is an extension of the first step but here you have to decide the tools and material that you would be using to build the prototype and those which you would use to build the final product. For example, to build quick mechanical prototypes, you might use 3D printing. Now, 3D printing uses photopolymer resin hardened by UV light. But in most cases, you would not want the final product to be made of that. Decide on the highest-quality yet most cost-effective option for your material.
Build a Miniature Prototype Yourself
If it is a physical object, before making an elaborate prototype, model it using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and then 3D-print it. It helps you understand even the smallest parts of your product and prepares you before you approach any prototyping professional.
Use Professional Services
Once you have a rough prototype, you may want to take it to the pros to get a more refined version and see how it would be manufactured once it moves to the mass-production stage. Vendors should be carefully chosen. They should not only be honest but also flexible enough to work within your budget. Check their credentials and past customer reviews. Make sure to get a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) from the vendor. This will serve as your legal protection if your prototype design gets stolen. At the end of the day, you should aim to have the most professional-looking working prototype so that it becomes easier to get more people on board.
Develop an In-House Team
For non-physical products like software, it is better to develop the necessary competency in-house instead of outsourcing the design and development work to third parties. Protection of design idea and product testing are more convenient with in-house teams.
Run Customer Tests
Just like in the case of idea validation, it might be useful to get customer feedback for your presentation prototype too, though the judgment lies completely with you if you want to run these tests. After all, you might not want to reveal your prototype to the customers at this stage. But it is better to get customer feedback as it helps you find defects and refine it further.
Prototypes are meant to be functional, not perfect and sometimes they can be expensive and time-consuming to build. But prototyping is the best way to get your idea in tangible form. It is an amazing experience to see an idea come to life. The focus should be to not have any preconceived notions and explore all possibilities and options available at this stage. The next phase for your start-up should be to go out in the market with your MVP to validate all your assumptions by using actual consumer data. Till then, happy prototyping!
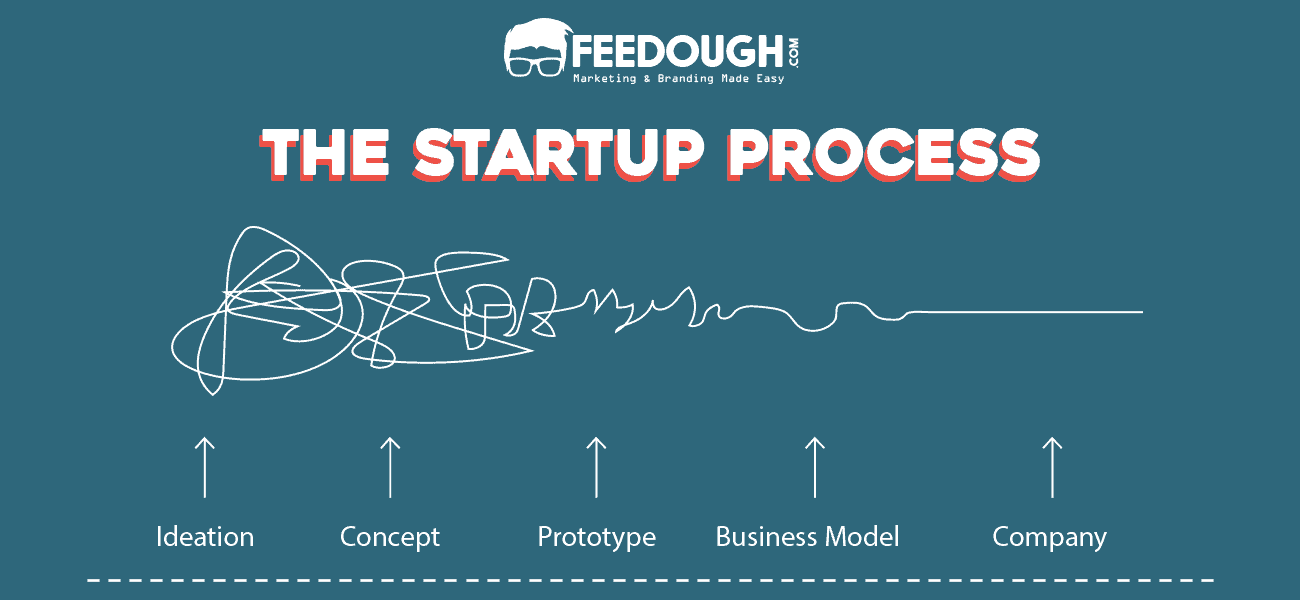
The Startup Process
We know how important your dream business is to you. Therefore, we’ve come up with an all in one guide: The Startup Process to help you turn your vision into reality.
Product Guy. Introverted Marketer. Engineer by education. Movie and TV Geek by nature. Can be seen reading comics and non-fiction books when not binging on movies and Netflix shows. Pop-culture junkie. Out and out foodie. Wee bit self-obsessed.”