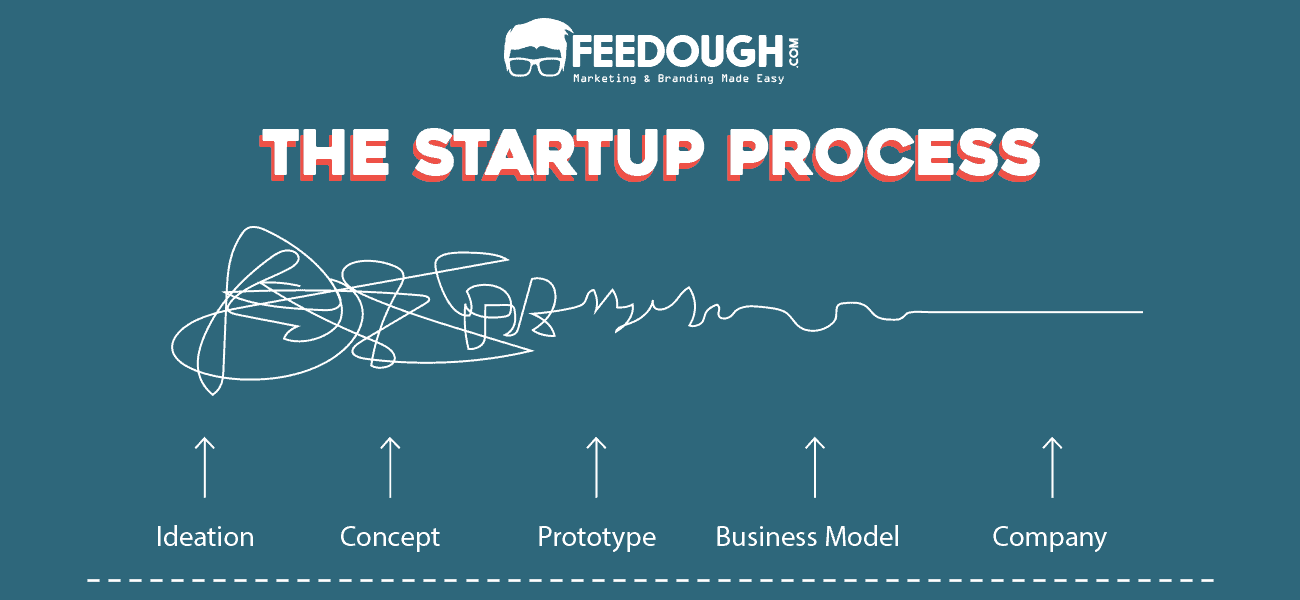
A startup is a new buzzword in the corporate world. Almost every entrepreneur who starts a new business calls his/her venture a startup.
But not every business is a startup.
Many entrepreneurs realize later that their business was nothing but a small business from the very start.
This creates a confusion of what exactly is a startup and how is it different from a small business.
Fret not as here’s a complete guide explaining the difference between startup and a small business.
What is a Startup?
A startup is a business structure powered by disruptive innovation, created to solve a problem by delivering a new product or service under conditions of extreme uncertainty. For example – Headspace, Duolingo, etc.
Precisely, it’s a business structure that has the following characteristics –
- Growth: Startup is a business structure designed to grow fast. According to Paul Graham, founder of Y Combinator, “A startup is a company designed to grow fast. Being newly founded does not in itself make a company a startup. Nor is it necessary for a startup to work on technology, or take venture funding, or have some sort of “exit.” The only essential thing is growth. Everything else we associate with startups follows from growth.”
- Business Model: Startups are known to have unconventional business models. This is because they venture into an untapped market or fulfil repressed demands of the market.
- Innovation: The mark of a true startup is disruptive innovation. Startups create new offerings or innovate the existing ones. They might also disrupt the way an offering reaches to the consumer and develop a new market for themselves.
- Uncertain Environment: Startups operate in a highly uncertain environment. The possibility of failure always hangs around an entrepreneur’s neck.
Any business structure that does not possess these four characteristics is not a startup.
What is a Small Business?
A small business is a privately owned corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship that requires less capital, less workforce, and little to no machinery. These businesses operate on a small scale to serve a local community and generate less annual revenue than a large corporation. For example, local grocery stores, hair salons, car garages, cafes, etc
Usually, a small business possesses the following characteristics –
- Limited Investment: Owners or a small group of individuals supply most of the capital requirements of the business. Since the scale of operations is small, the capital requirement is less.
- Labor-Intensive: Small businesses usually don’t require heavy or sophisticated machinery. It uses more labour-intensive techniques.
- Less Number of Employees: Small businesses employ a smaller number of employees as compared to large corporations. This is mainly due to their small scale of operations.
- Local Area of Operations: Businesses like groceries shop, bakeries, or hair salons are all small businesses. They operate locally and remain there for longer periods of time (years or maybe decades), this helps the businesses to build a strong relationship with local customers.
- Management: In most cases, the owner is also the manager of the business, which helps in quick decision making.
Startup vs Small Business
Small business don’t operate in an uncertain environment, have a traditional business model, and doesn’t grow at a substantial rate. They are just small business structures that have nothing special in them.
Startups, on the other hand, are special business structures that change the way the market, economy, or the world works.
Intent
The intention of the entrepreneur is where the distinction arises between small businesses and startups.
Startup | Small Business |
|---|---|
The intention behind a startup is to disrupt the market with a scalable and impactful business model. | The sole intention of a small business’ owner is to be her/his own boss and secure a place in the local market. |
Innovation
Startup | Small Business |
|---|---|
Innovation is an essential part of startups as they always create a new unique offering or innovate an existing one. | Small businesses deal in offerings that already exist in the market. |
Business Model
Startup | Small Business |
|---|---|
Startups usually have unconventional business models that are new to the market. This puts a startup in a high-risk position. | Small businesses adopt a tried and tested business model which creates a less risky situation. |
Growth Rate
Startup | Small Business |
|---|---|
Startups witness an exponential growth which is without any limits.The biggest example is Facebook. After its launch, it grew exponentially throughout the world. | Small businesses grow slowly and steadily. Their purpose is to maintain a steady income; therefore, the growth rate stops after reaching a certain level of income. |
Source of Funding
Startup | Small Business |
|---|---|
Startups go through various rounds of equity funding. Their sources are angel investors, venture capitalists, corporates, etc. | Small businesses acquire funds only in the initial stages of the business. Once established, they are either revenue financed or take business loans. They don’t go through various rounds of equity funding like startups. |
Revenue
Startup | Small Business |
|---|---|
A startup takes years to plan, collect funds, build a product, and execute. Therefore, it generates revenue in the later years. | Small businesses make profits from the start since they operate on tried and tested business models, and provide offerings that already have a market. |
Technology
Startup | Small Business |
|---|---|
Startups are often tech-oriented. Usually, startups use technology to disrupt the market. | Small businesses use traditional methods or minimum use of technology. The technology used in these businesses tends to be simple. |
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on startup vs small business in the comments section.
A budding entrepreneur who loves to read. He has a knack for research work, writing, and creating his own music.


![How To Get Startup Funding [The Complete Guide] startup funding guide](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/startup-funding-guide.png)